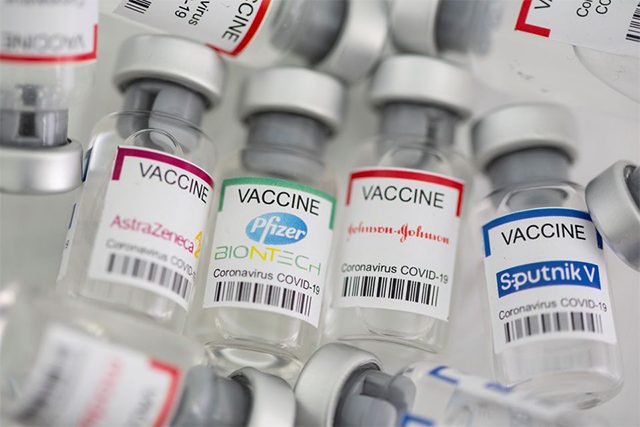
When we were hanging out for a COVID-19 vaccine in 2020, it was a bit like a horse race. We asked ourselves which vaccine would get over the line to win, and how quickly. Then, as multiple vaccines began reporting results from clinical trials, the race turned to which could offer superior efficacy and safety.
Flash forward to 2021, with multiple safe and effective vaccines approved, parts of the globe are experiencing “brand tribalism”. Which brand of vaccine you want, or can get, has become a hot issue.
In the United States, young vaccinators post their vaccine “team” or “tribe” preferences on social media, saying, “only hot people get the Pfizer Vaccine”.
In Britain, the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine invokes patriotism as well as warm feelings about its not-for-profit roots, even as some consumers prefer the “fancier” Pfizer vaccine.
In Hungary, fraught cold war politics have resurfaced as consumers can be vaccinated with one developed in the East or West.
In Australia, we’ve seen something different. Since the move away from the AstraZeneca vaccine for people under 50 announced in April, brand preferences became about safety rather than efficacy.
However, data from our research currently under peer-review and reports from elsewhere show younger and ineligible people are still stumping up to try and get vaccinated with whatever vaccine they can get.
The public isn’t so tuned in to flu vaccine brands
Having numerous brands of a particular vaccine is not new. Every year, multiple brands of influenza vaccines are used across various age groups.
One of us (Carlson) has been interviewing people about influenza vaccination for over five years, and no participant has told her they prefer a specific brand.
Things are different with COVID-19 vaccines, as people are increasingly aware of the different brands available to them and others. Through our Coronavax project, we are continually hearing brand names mentioned.
Yet some participants challenge the focus on brands. Alma*, a 50-year-old doctor, told us:
No one normally cares what brand of vaccine you get! With the flu vaccination […] people don’t start quizzing me on “what brand is this one?”
Other participants, such as 71-year-old Frank*, were critical of the emphasis on brands. When asked his opinion on under 50s receiving Pfizer and over 50s receiving AstraZeneca, he turned the tables. He asked his interviewer (McKenzie) if she had received her flu vaccination this year (she had) and whether she knew which brand she had received (she did not).
Others expressed some brand preferences, and all were very aware of the different brands.
The difference with flu vaccines, we hypothesize, is that although health-care providers are told about the different influenza vaccine brands so they can safely vaccinate people with the age-appropriate vaccine, the brands themselves are never front page news.
Flu vaccine brands are only ever sold to consumers as “the” flu vaccine. But COVID-19 vaccine brands feel like a buffet in which consumers don’t actually have much choice.
Vaccine preferences in Australia
International examples of COVID vaccine “teams” and people sharing their vaccine allegiances don’t directly translate to Australia. That’s because here, brand availability cannot be divorced from systemic and vaccine supply problems, such as not having enough of the appropriate vaccines for the specific age groups requiring them.
So in Australia, we don’t see brand tribalism as a fun expression of identity that can help orient everyone towards vaccinating.
Rather, brand preferences in Australia have developed through changing vaccine recommendations, and positive or negative news coverage.
In this imperfect scenario, governments need to keep backing the available vaccines that people can safely receive according to their age and risk profile, not encouraging people to wait for new ones.
Any pros of brand awareness?
One of the few benefits in the brand “team” wars is Australians are generally more aware of the science behind the development and safety of vaccines.
Most people we interviewed had recently learnt more about the science of vaccination. And most planned on being vaccinated with what was available to them, when it was (easily) available.
We hope this improved scientific literacy can help people appreciate the expertise that goes into creating vaccines, as well as the work of people like us who study their rollout, acceptance and uptake.
However, brand preference tribalism isn’t going to help Australia get vaccinated. Our unique situation of (necessary) directives about specific vaccine brands for different ages, our low rates of disease, and the increasing cut-off age for the AstraZeneca vaccine announced recently have contributed to a broken roll-out strategy.
The conversations we need to keep having about brands are difficult ones. We are on quicksand and science keeps evolving. The most important message isn’t about which team is better. It’s about having a responsive system that cares about people. It changes things up when it needs to, however challenging that makes our vaccine rollout.
What we can do right now
The best thing we can do is to tone down the brand narrative within the significant constraints we face. All COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective, and if the disease profile of our country changes, then the recommendations about who should have which vaccine may change again. All COVID-19 vaccines protect and benefit individuals and communities.
Most importantly, all Australians benefit when we can safely reopen to the world and to our local businesses and communities. Without painful lockdowns, vaccines are all we have to look after ourselves and each other. We’re on that team.
*All names of research participants are pseudonyms.![]()
Katie Attwell, Senior Lecturer, The University of Western Australia; Lara McKenzie, Research Fellow, School of Social Sciences, The University of Western Australia, and Samantha Carlson, Post Doctoral Research Officer, Telethon Kids Institute. This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.